FORMATION OF FREE RADICALS CONCEPT AND MANAGEMENT
18-01-2026 12:00:00 AM
Whatever unnatural man is giving to the nature, the same is being rebound in the form of new diseases. The medical scientists engage continuously to find solutions. The conception of disease and its pathogenesis, change daily ranging from the bacterial or viral invasion to the idiopathic. Older hypotheses are replaced by newer ones, make it an ongoing process in establishing a disease and finding an appropriate management system. The concept of free radicals is considered the basis for number of diseases, (such as neurodegenerative, chronic inflammatory, cardiovascular, cancer, ischaemic heart diseases, atherosclerosis, ageing, tumour, hepatic disorders, liver diseases, ascites, anaemia, diabetes and rheumatism), forming one of the new therapeutic strategies to streamline their role in the body metabolism.
Free radicals are highly reactive, electrochemically unstable atoms and molecules with presence of unpaired single electron spinning at great velocities, around the core in outer orbits causing a tendency to react easily. Most stable chemical compounds contain paired electrons in these orbits. When a free radical encounters other molecules, it is usually extremely damaging, for it causes other free radicals also to react, setting off a chain reaction. Most free radicals, unlike foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses, are produced as a normal part of the body’s use of oxygen, while non-oxygen-based molecules and atoms too generate the same.
In healthful conditions, enough of these components are used up in the body, some are killed by bacteria or viruses and the defence mechanism of the body acts upon them, so the life processes go on. The main protective enzymes which the body uses to counter the effect of excess free radicals are Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Catalase and Glutathione peroxidase which scavenge and neutralize when in excess. If the defence mechanism of the body fails to combat them or they are not properly utilized in the body, these tiny silent killers pose a threat by injuring tissues, their proteins and fat, RNA, DNA, producing disease conditions.
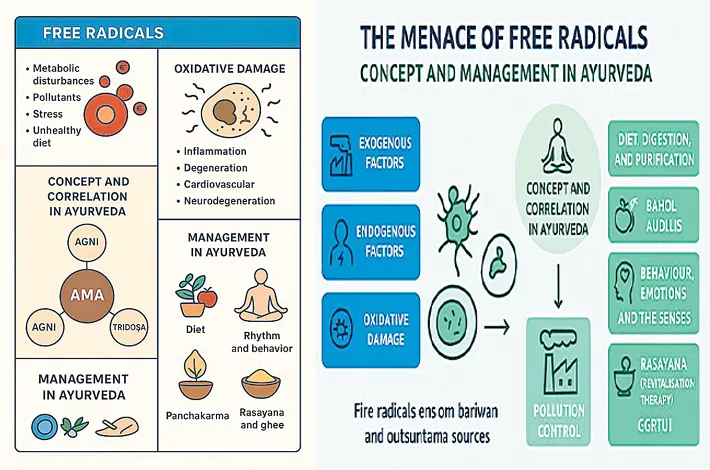
Indian system of medicine considers that all the diseases are caused by the derangement of metabolism (agni) and nourish the body through this, so that the life and death of an individual depends upon its proper or improper functioning. The central gastro-intestinal metabolic factors i.e., bhutagnis and seven tissue metabolic factors i.e., dhatwagnis, constituting the thirteen types of agni. To maintain the nourishment of the body tissues, nutritive and waste products formed in the process of digestion and metabolism, support each other.
Metabolic processes may be defective at three levels, (a) gastrointestinal tract, (b) intermediary in the liver and (c ) tissues. The product of metabolic disorder is technically called “ama” meaning “unripe” (putrified and poisonous) i.e., “defective or incomplete metabolism”, forming the basis of every type of disease mentioned above except those which result from direct trauma. The superfluous production of free radicals can be correlated with the production of “ama” which is “acute” to begin with and tending to become “chronic”.
In the “acute” condition it may cause the disease conditions like fever, diarrhea and dysentery etc., in the “sub-acute and chronic” form may lead to mal-absorption and chronic diseases. The “ama” having the precursors of different diseases in the form of highly reactive free radicals is the initiator in the neurohumoral, metabolic and cytoplasmic events (tridosas). The improper enzymatic and hormonal activity including that of enzymatic free radical scavengers and decreased defense mechanism of the body (ojakshaya) at the cellular level are the important factors to allow the free radicals to cause havoc in the form of different diseases.
The strength of the enzymatic activities at the cellular level (dhatwagni) depends upon the central gastrointestinal metabolic factors (jatharagni) and the defence mechanism (ojabala) depends upon the proper digestion of the nutritive elements, their uninterrupted delivery to the target cells which subsequently results into the replenishment of the body tissues. The management of free radicals aims at correcting both internal and external environment of the body to become unison with the nature.
As excellent food and digestion are critical to robust health, different techniques for improving digestion and treating digestive disorders include the selection of proper food according to the digestive capacity (agnibala) of an individual. Proper conversion of food depends upon the potency of the jatharagni. Impaired digestion and metabolic processes involve the concept of appetizer and digestive (dipana and pacana) drugs. Maintenance of different levels of metabolism restricting the formation of “ama”, ensures the proper activity of enzymatic free radical scavengers.
To render the body free from “ama”, pollutants and other pathogenic impurities, if accumulated, five purufucation processes (panca karma therapy) have been detailed. The ideal health involves the orchestration of billions of elements- cells, nerves, muscles, ligaments, bones, joints, tendons, organs, glands, system, humors and senses by intelligently observing the circadian (dinacarya and ratricarya) and circannual (ritucarya) rhythms. This idea of a connection between patterns of order in nature and in the human body was clear to the physician seers of Indian Medicine millennia ago.
Human body is not a frozen lake, it is a turbulent river of ever-changing thoughts, emotions, sentiments, moods, priorities, loyalties and interests and depends upon the psychic traits such as intelligence (satvika), energy (rajasika) or dullness (tamsika). Because of this only “stress” has been laid down in the Indian scriptures – satvika, is characterised by knowledge, critical scientific reasoning, courage and sharp memory. Fibrous and vegetarian diet and fruits are rich in these qualities which increase intelligence (satva guna) thereby limiting the production of free radicals and induction of natural free radical scavengers.
While ageing and death are inevitable, this sort of lifestyle and mental make-up surely and certainly delays the process of ageing and disease, adding life to the years, to live hundred years like ancient seers. It is purely on account of satva guna that qualities like mental equipoise, clarity of thought, assertiveness, cheerfulness, power of reasoning etc are generated. Apart from it, the mental illusion by negative thoughts such as those of jealousy, anger, greed, possessiveness, stressful conditions are accompanied by high plasma levels of glucocorticoids and catecholamines, increase lipid free radicals and reduction of natural free radical scavengers.
It contributes to the longevity, promotion of memory and intelligence, immunity against disease and decay, preservation of youth, lustrous complexion and voice and optimum strength of the body and senses. It confers “the capacity for the achievement of what is said” and “the command of the respect and regard of people” and the promotion of bodily glow. In this series, several drugs have been prescribed to be used in different ways. The important among them are Bacopa mennieri, Linn (Brahmi), Ocimum sanctum, Linn (Tulsi), Withania somnifera, Dunal (Ashwagandha), Tinospora cordifolia, Meirs (Guduci), Acorus calamus, Linn (Vaca) and Phyllantusembilica, Linn (Amaliki). Various scientists and researchers from different disciplines have proved their efficacy as immunomodulators, antistress and adaptogenic agents which decrease acetyl choline, catecholamines, 5 HT levels and increase serotonin and endorphins in the brain tissue.
Once the immune system is potentiated, the menace of free radicals will be largely solved. The alien concept of discarding the use of clarified butter (ghee) and the use of unsaturated fats as cooking medium or otherwise also does not hold good. In Indian Medicine, many medicines are either prepared in ghee or contain ghee as major constituent. It has now been proved that digestion, absorption and delivery to a target organ is crucial in obtaining the maximum benefit from any formulation, facilitated by ghee. Since active ingredients are mixed with ghee, they are easily digested and absorbed. Lipophilic action of ghee facilitates transportation to a target organ and final delivery inside the cell as cell membrane is a lipid.
This nature of ghee facilitates entry of the formulation into the cell and its delivery to the mitochondria, microsome and nuclear membrane. In the process of evaluating the activities of natural compounds, it has been found by sophisticated research that when herbs are mixed with ghee, their activity and utility get potentiated many times. Ghee contains carotene and vitamin E and known antioxidants. In Ayurvedic texts the properties of ghee are given in detail. Bhavaprakashaka, an authority on Ayurveda says, “Ghee is a rejuvenator, tasty, good for eyes, digestive stimulant, supports glow and beauty, enhances stamina and sharpens memory, protects the body from various diseases and promotes longevity”.
We find Carvaka Darsana saying, “Yavata Jiveta Sukhama Jiveta, Rnama Krtva Ghrtama Pibeta (as long as you are alive, live happily and use ghee even at the cost of borrowing)”. Although said in some different context yet is advocates the regular use of ghee. https:// kitchencrafthubs. com/is-ghee-supposed-to-be-solid-or-liquid/ It is known that an acute myocardial infarction and revascularisation (affected either by surgical bypass, balloon angioplasty or thrombolytic therapy) cause ischaemia and reperfusion myocardial injury, leading to a sudden burst of oxygen free radicals.
The same probably applies to patients suffering from cancer and other degenerative diseases. If we could find out these people in the formative stages and give them extra free radical scavengers like SOD, we could prevent them. Ingestion of tablets of SOD is not the solution, as the high molecular weight enzyme, gets broken down by digestive juices and becomes ineffective. It cannot be injected as the desired effect is not achieved due to half-life being only 6 min and most of it is excreted by the kidneys before it reaches the site. Naturally, we require a scavenger of free radicals which has an ease of administration with a prolonged and sustained effect.
The herbal preparations in different forms such as powders, tablets, fermented liquids, confections etc, are serving the purpose and are ready to face any challenges in the wake of any new pathological condition. It is still not realised that plants and herbs grown in proper sunlight have large quantities of free radical scavengers like SOD and other antioxidants, trapped within their polymer structures. To make low molecular weight antioxidants, special methods of slow heating with uniform gentle stirring have been advocated.
By adopting such techniques, large quantities of enzymes protease and amylase are released which split these polymers and make such antioxidants for the oral use. This plant power which the present day science has started realizing is being used by the physicians of Indian Medicine since the time of the Vedas. Not only free radicals are formed during metabolism of nuclei of living cells and the membranes of phagocytes, but they are also produced by insecticides, weed killers, anti cancer agents, chemicals used in processed foods and majorly atmospheric pollution, unless they are acted upon by antioxidants in the body or above mentioned are controlled.
To sustain the living process, oxygen or prana vayu is an utmost necessity. Though ecologists and environmentalists have realized this fact, ozone layer depletion due to wastes of industrial produces and deforestation has plateaued, it has aroused a consciousness. Returning from chemical fertilizers, chemical pesticides, processed, preserved and fast foods to the conventional foods, the use of bioactive manure and insecticidal techniques derived from plant kingdom are the positive signs of change.
— Dr Swarnabala Ganti
— Dr Rambabu T
— Dr Anahita Bharadwaj
Swaram Biochem, Secunderabad








